Now, let's me talk about measurement unit that used in telecommunication, especially in VSAT.
dB (deciBell) unit copes with logarithmic and relative parameter.
dBm is a standard unit for measuring levels of power in relation to a 1 milliwatt (mW) reference signal. dBm and dBW related to "absolute" power/level.
0 dBm (=mW) means power of 1.0 mW
dBm is similar to dB, or decibel, except that where dB is relative to the power of the input signal, dBm always relates or absolute to a 1 milliwatt signal (as measurement unit).
A minus sign before the dBm indicates a loss and a plus sign or no sign at all before the dBm indicates a gain.
A guide in this relative unit can seen below :
10 dB means 10 times than original
7 dB means 5 times than original
3 dB means 2 times than original
1 dB means 5/4 times compared to original
0 dB is 1X the original
-1 dB means 4/5 times compared to original
-3 dB means 1/2 times than original
-10 dB means 1/10 times than original
example:
- 0 dBm = 1mW (0 dB always means = 1)
- 30 dBm = (10dB + 10 dB + 10 dB) or (10 x 10 x 10 ) = 1000 mW = 1 W
- 0 dBW = 1 W
- 37 dBm = (10 dB + 10 dB + 10 dB + 7 dB) or (10x 10x 10x 5) = 5000mW = 5 W
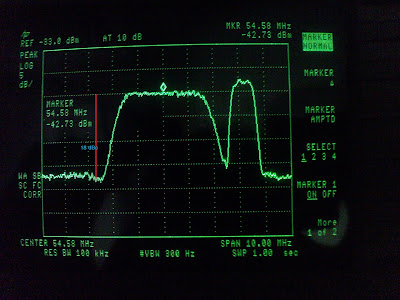
There is another unit of measuremen, dBc, which is the power ratio of a signal to a carrier signal, expressed in decibels. If the dBc figure is positive, then the relative signal strength is greater than the carrier signal strength. If the dBc figure is negative, then the relative signal strength is less than carrier signal strength.
Look at the picture below,
the different between the the carrier signal to noise floor is 18 dBc.

Comments
Post a Comment