There are many types for earth station antenna, which are :
1. Prime Focus Feed
- Most popular due to its excellent efficiency (approximately around 62%)
- Because of its relatively large surface, the prime focus antenna is less sensitive to small directional deviations and there is a better chance of receiving signals outside the normal footprint.
- Usually limited up to 4.5 mtr diameter
- Sometimes problem with OMT adjustment for "prima" Cross-Polar Isolation (CPI) characteristics
- Because of the LNB is mounted centrally, a lot of the incoming signals are blocked by the LNB on the way to the antenna surface.
2. Offset Feed
- Better efficiency due to reduction of Feed (and spars) "blocking"
- Simple to deploy, usually to Fly-away or Transportable SatCom terminals
- Much easier to adjust in achieving very accaptable Cross-Pol Isolation (CPI)
- Due to its simple construction, while satisfying the requaired ruggedness of Feed support, normally these are produced max on 3.8 mtr diameter
- Usually the offet degree is 22 which means that the beam comes off the dish at an offset angle of 22 deg
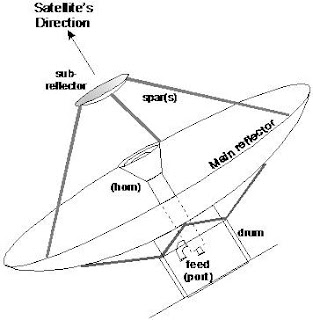
3. Cassegrain / Gregorian Feed
- This type of Feed is usally used for Antenna's aperture larger than 4.5 mtr
- Very safe (in radiation aspects)
- Relatively very convenient in CPI set-up
- Cassegrain antenna is a double reflector system which works on the principle of Cassegrain optical telescope
- The main advantages of Cassegrain antenna are a reduction in the axial dimensions of the antenna just as in optics and a greater flexibility in the design of the feed system
- The difference between Cassegrain and Gregorian is on the secondary reflector. Cassegrain is convex secondary reflector while Gregorian is concave secondary reflector
Example of Gregorian type Antenna







Good info. I have a question.
ReplyDeleteDo you know if the applications on cell phone give sattelite position relative to true North or magnetic North or the set angle of the dish itself with its correction (22 degree)? Thanks